HSEA MODEL
CREATTION
From Model Creation to Operation
About HSEA Model
Hybrid SEA Model(HSEA Model)
Analytical SEA Model
SEA model created using the theoretical formula of SEA based on the material information of panels and soundproof materials
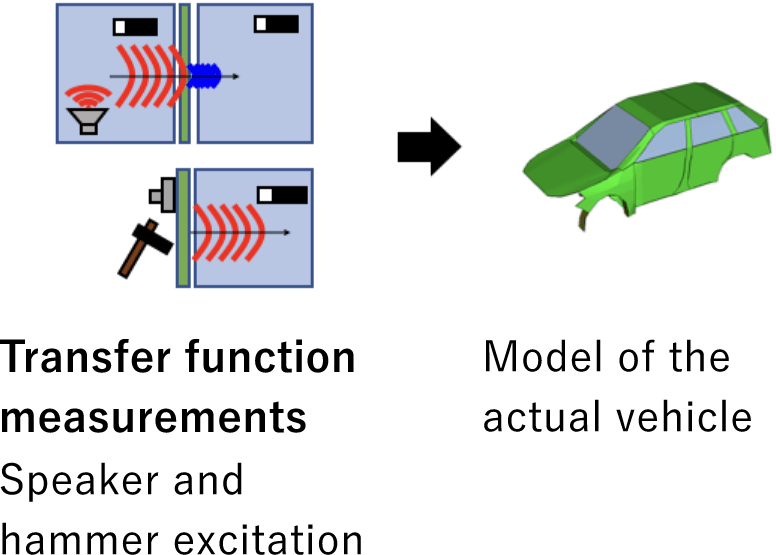
Experimental SEA model
SEA model that has adjusted SEA parameters to describe the transfer function measured by speaker / hammer excitation
Various contents can be accurately analysed by combining the 2 models.
Role of HSEA Model
Use the Statistical Energy Analysis (SEA) model to calculate useful outputs for a variety of inputs
Imput Example
- Road noise
- Engine noise
- Gear/motor noise
- Wind noise
- On Road Driving noise
- Clutch noise
- Power seat noise
Output Example
- Sound Pressure Level(SPL)
- Vibration Velocity Level(VVL)
- Contribution
- Power Flow
Advantages of the HSEA model
It is possible to investigate the effects of soundproof materials modification and create specification proposals to achieve the target performance with hight accuracy and without additional experiments.
Experimental man-hours and costs significant reductions are possible
Model creation
Analytical SEA Model
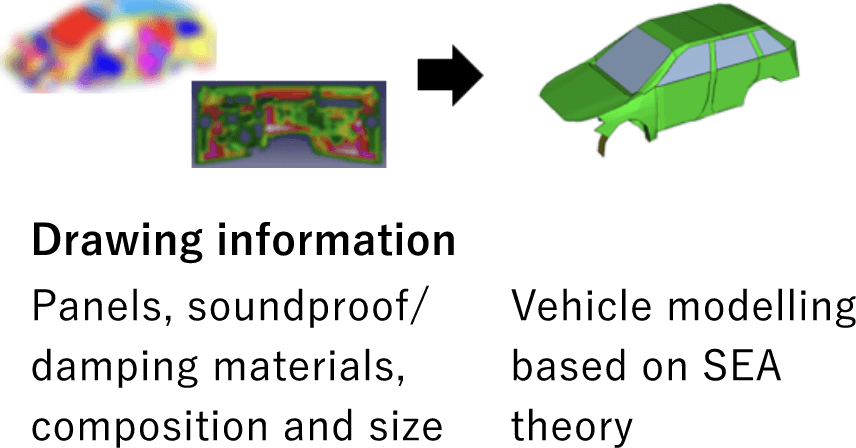

Experimental SEA model
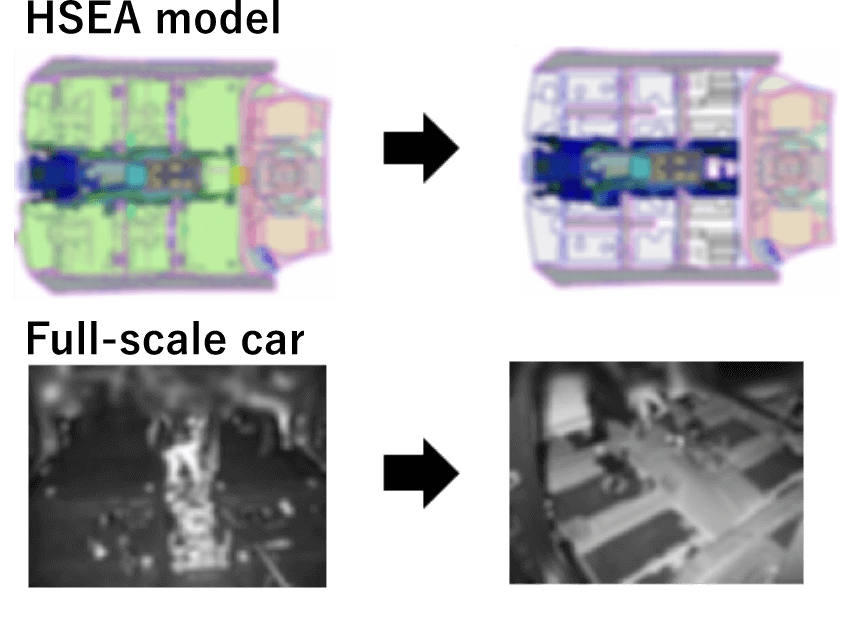
Design Modification Process
(DM experiment)
Compare the changes in specification modification between model predictions with experiment
- Removal of soundproof material
- Adding soundproof material
- Leak masking
Example: Floor carpet removal
Guaranteed accuracy of
HSEA models
Final HSEA model
completed
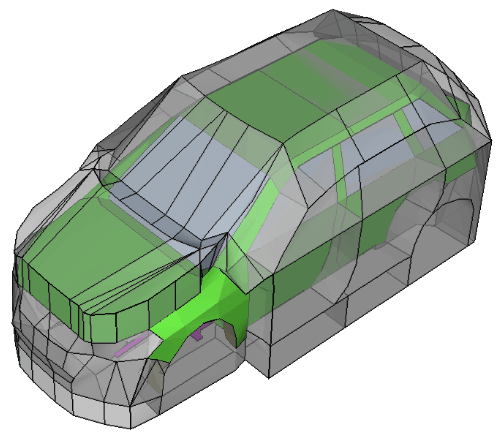
Experimental SEA model (Overview)
➀ TDLF and ➁ CLF are adjusted to experimental results in Experimental SEA model
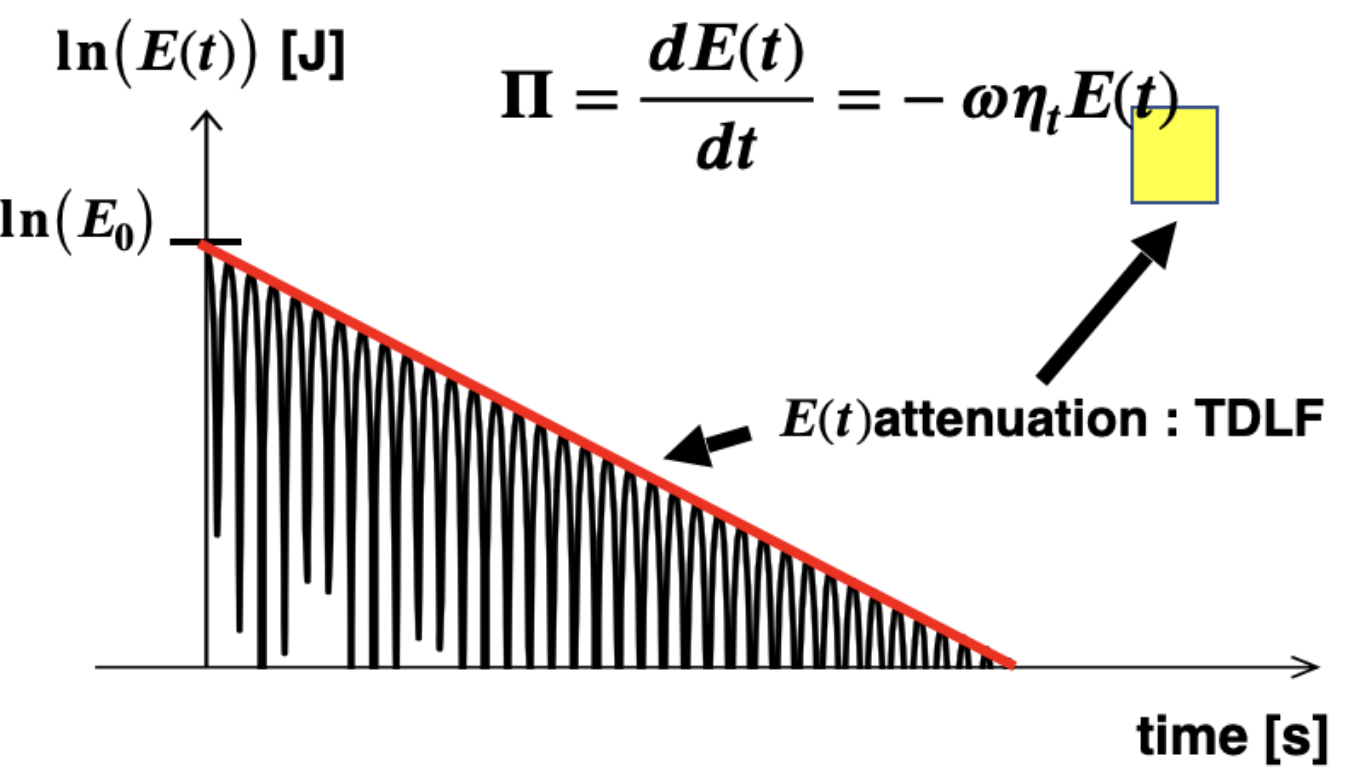
➀ TDLF
Determined by the magnitude of decay of Energy with respect to time.
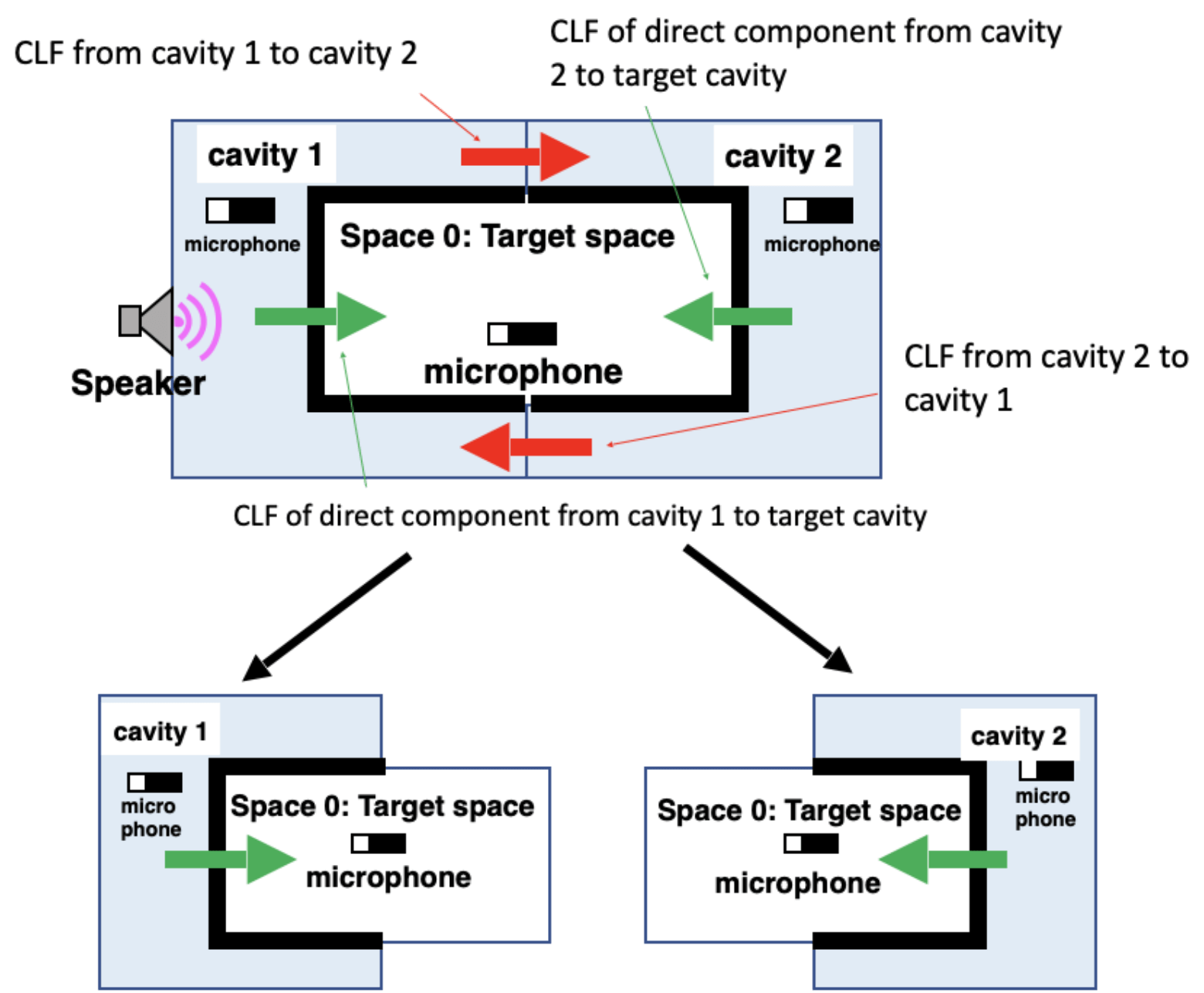
➁ CLF
Determined by multiple transfer function measurements. Model is performed by extracting only the direct components (= indirect component removal)
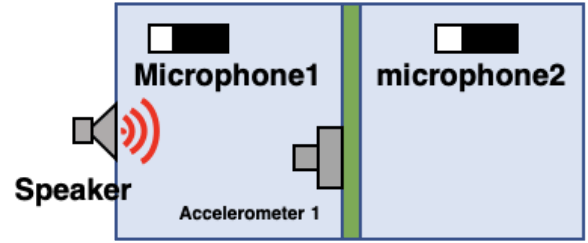
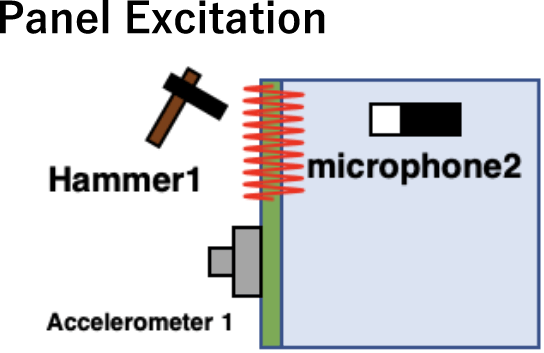
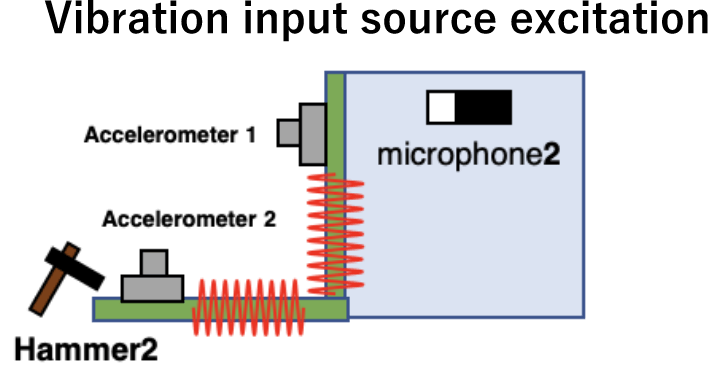
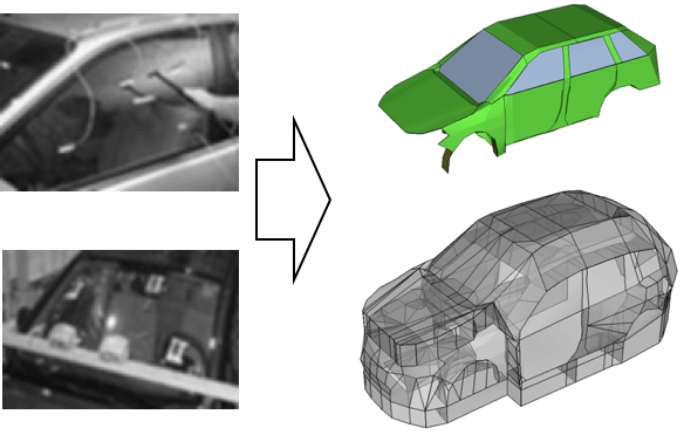
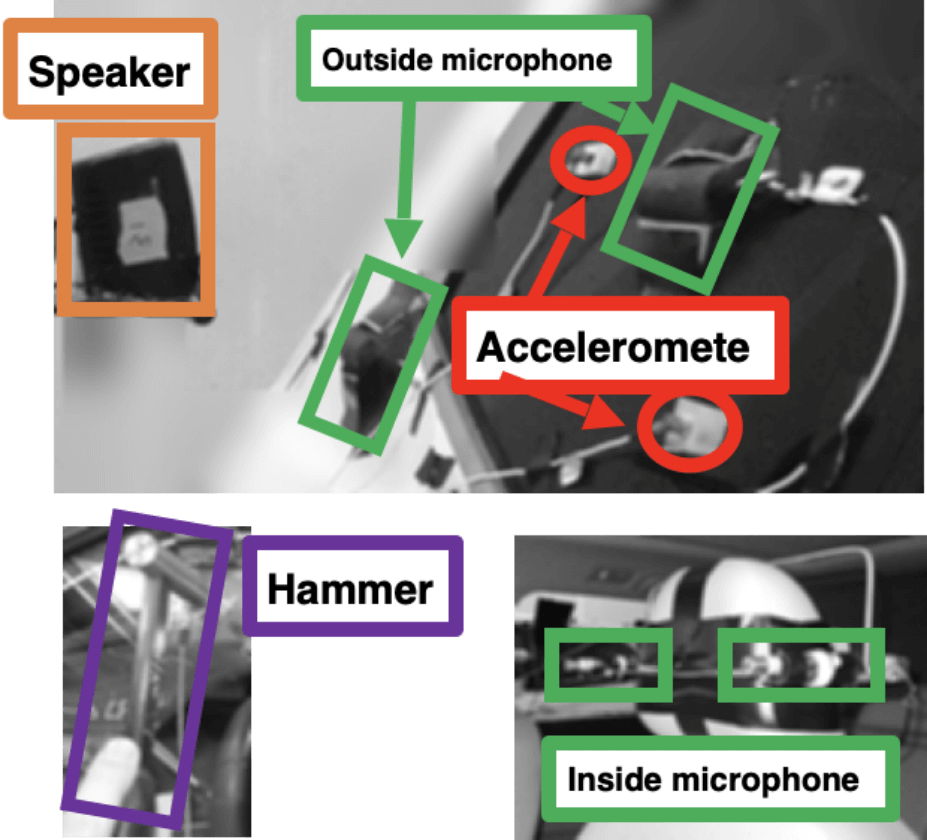
Experimental SEA model (excitation experiment and sensors)
| Speaker Excitation |
Measurement data ・Acoustic-acoustic transfer function |
|---|---|
| Hammer Excitation |
Measurement data ・Acoustic-acoustic transfer function |
|
Measurement data ・Acoustic-acoustic transfer function |
Speaker, hammer, interior/exterior microphones, accelerometer photo
Example:
Number of sensors
(Vehicle model: K and A created in 2020)」
Microphones: 131 (inside: 39, outside: 92)
Accelerometers: 259
Analytical SEA model and experimental SEA model
Important features of the HSEA model
Allows performance evaluation on the entire vehicle body of specification changes
The following methods are used to evaluate the performance of the entire vehicle body by combining the analytical SEA model with the experimental SEA model.
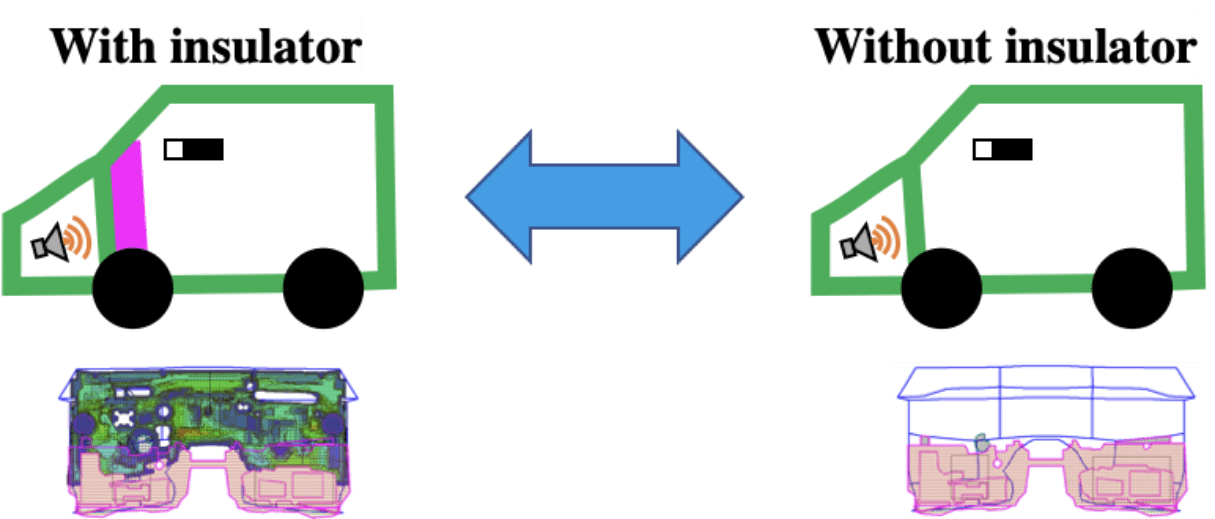
Example: Modification of Dash insulator specification
1. Calculate the parameters before and after the specification change using the analytical SEA model.
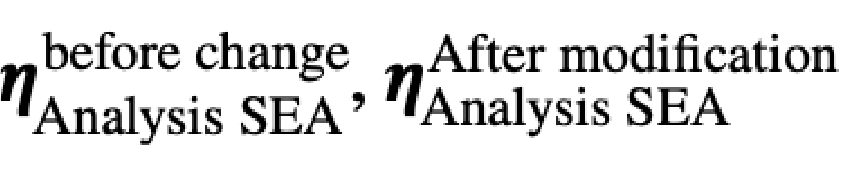
Predicted parameters of the experimental SEA model after specification changes.

DM experiment
Example:
Comparison of SPL in vehicle before and after removal of the dash insulator
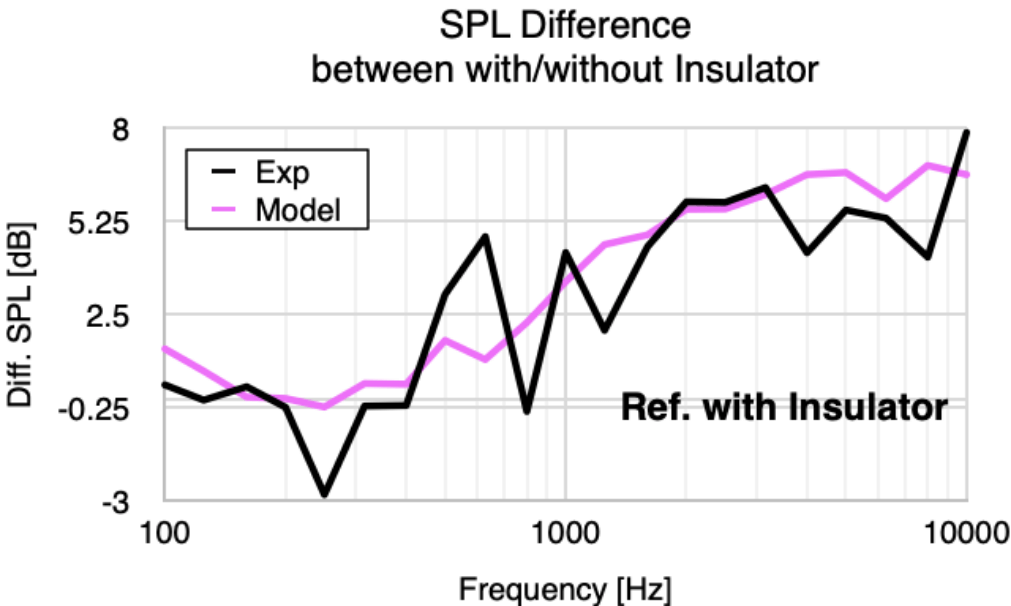
Confirmation that the amplitude of worsening with insulator removal is predictable.
Guaranteeing accuracy of HSEA model by DM experiment